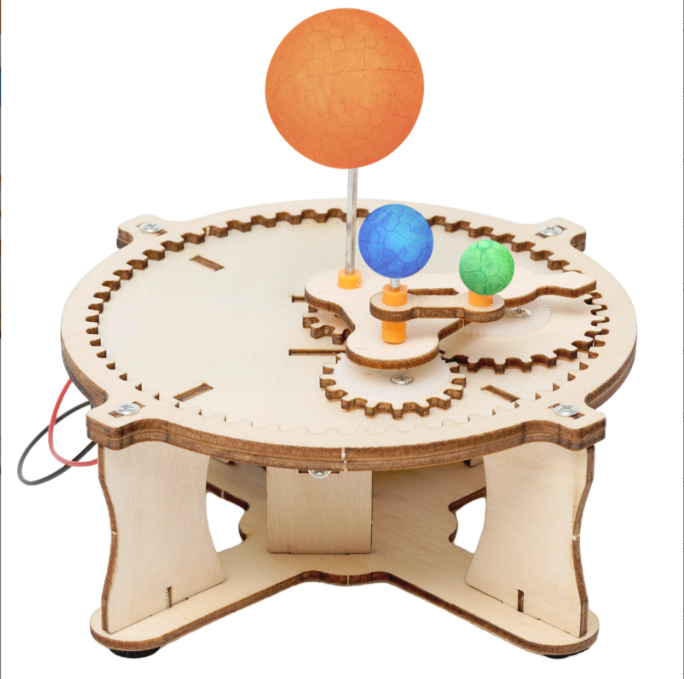
SwitchedOnToys – Earth Month Sun : The motorized orrery featuring the Earth, Moon, and Sun mounted on gears is an excellent example of cost-effective learning and STEM education. This model vividly demonstrates the fundamental aspects of celestial mechanics, including orbits, phases of the moon, eclipses, and seasons.
As an easy-to-assemble kit, the orrery provides a hands-on experience with astronomical concepts. The gear-driven movement of the Earth, Moon, and Sun offers an engaging and intuitive way to explore the relationships and motions of these celestial bodies.
Key features include:
-
STEM Learning: This model visually represents the dynamics of the Earth-Moon-Sun system, enhancing students’ understanding of celestial mechanics through interactive learning.
-
Hands-On Experience: Assembling and operating the motorized orrery allows learners to observe the relative motions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun, making complex astronomical phenomena more accessible.
-
Educational Value: The model serves as a valuable teaching resource, illustrating key concepts such as orbits, phases, eclipses, and seasonal changes in a clear and effective manner.
-
Innovative Design: The use of gears to simulate celestial movements provides a practical demonstration of how mechanical systems can model complex astronomical interactions.
Overall, the motorized orrery is a dynamic educational tool that combines simplicity with functionality, offering an engaging way to explore and understand the relationships between the Earth, Moon, and Sun.
Components of the Model
-
Sun: Represented by a large, stationary ball positioned at the centre of the model.
-
Earth: A smaller ball that revolves around the Sun.
-
Moon: The smallest ball that orbits the Earth.
Key Movements Illustrated by the Model
-
The Earth revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit, taking about 365.25 days to complete one full revolution.
-
This motion, combined with the tilt of Earth’s axis, explains the cycle of seasons.
Moon’s Orbit Around the Earth:
-
The Moon orbits the Earth approximately every 27.3 days, known as a sidereal month.
-
Due to tidal locking, the Moon’s rotation is synchronized with its orbit, so the same side always faces Earth.
Phases of the Moon:
-
As the Moon orbits Earth, varying portions of its surface are illuminated by the Sun, resulting in different moon phases such as new moon, crescent, first quarter, gibbous, and full moon.
Eclipses:
-
Solar Eclipse: Occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, casting a shadow on Earth.
-
Lunar Eclipse: Occurs when Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon.
Educational Uses of the Model
Visualizing Orbits:
-
Helps students understand the elliptical orbits of the Earth around the Sun and the Moon around the Earth.
-
Illustrates how these relative positions change over time.
Explaining Seasons:
-
By tilting the Earth’s axis in the model, students can see why different parts of the Earth experience different seasons.
Understanding Moon Phases:
-
Shows how the Moon’s position relative to the Earth and the Sun affects the phases of the Moon observed from Earth.
Eclipses:
Demonstrates the alignments required for solar and lunar eclipses and explains why eclipses don’t occur every month.
 100% Australian owned
100% Australian owned










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.